Within The Complex Realm Of Computer Networks, The Network Operating System (NOS) Is Essential For Enabling Inter-Device Communication, Resource Sharing, And Management. In Order To Simplify The Complicated World Of Network Operating Systems, This Thorough Book Offers A Methodical Examination Of Their Features, Advantages, And Real-World Uses.
An Overview Of Network Operating System Understanding
A Network Operating System (NOS) Is Fundamentally A Specialized Software Platform Created For The Purpose Of Managing And Overseeing Network Resources And Services. In Contrast To Conventional Operating Systems, Which Are Mainly Concerned With Individual Computer Systems, Network Operating Systems (NOS) Address The Particular Needs Of Networked Devices And Provide Smooth Communication And Cooperation.
A Network Operating System’s Functions
A NOS coordinates the activities of multiple computers across a network. This can include such devices as PCs, printers, file servers and databases connected to a local network. The role of the NOS is to provide basic network services and features that support multiple input requests simultaneously in a multiuser environment.
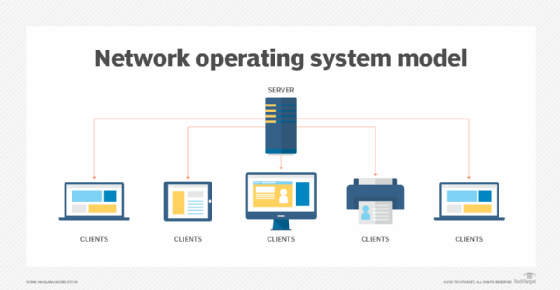
Types of network operating systems
There are two basic types of network operating systems:
- Peer-to-peer (P2P) network OSes let users share network resources saved in a common, accessible location. In this architecture, all devices are treated equally in terms of functionality. P2P usually works best for small and medium LANs and is less expensive to set up compared to the client-server model.
- Client-server network OSes provide users with access to resources through a server. In this architecture, all functions and applications are unified under one file server that can be used to execute individual client actions, regardless of physical location. Client-server tends to be more expensive than P2P to set up and requires significant technical maintenance. An advantage of the client-server model is that the network is controlled centrally, which makes changes or additions to technology easier to incorporate.
Resource Sharing:
- One Of The Primary Functions Of A Network Operating System Is To Facilitate Resource Sharing Among Connected Devices.
- This Includes Sharing Files, Printers, Scanners, And Other Peripheral Devices Across The Network, Enabling Users To Access And Utilize Resources From Any Location Within The Network.
User Authentication And Access Control:
- NOS Implements User Authentication Mechanisms To Ensure That Only Authorized Users Can Access Network Resources.
- Access Control Policies Are Enforced To Regulate User Permissions, Specifying Which Resources Each User Can Access And The Actions They Can Perform.
Directory Services:
- Network Operating Systems Often Incorporate Directory Services That Centralize User And Resource Management.
- Directory Services Maintain A Directory Database Containing Information About Users, Groups, Devices, And Network Resources, Facilitating Efficient Management And Organization.
Network Communication:
- NOS Facilitates Communication Between Devices Within The Network Through Protocols And Services Such As TCP/IP, UDP, DNS, DHCP, And Others.
- It Ensures Reliable Transmission Of Data Packets, Routing, Addressing, And Error Detection And Correction To Maintain Network Connectivity And Performance.
Types Of Network Operating Systems
Client-Server NOS:
- In A Client-Server Network Architecture, Client Devices Rely On A Centralized Server To Access Network Resources And Services.
- Examples Of Client-Server Network Operating Systems Include Windows Server, Linux/UNIX Servers, And Novell Netware.
NOS Between Peers:
- Peer-To-Peer (P2P) Network Operating Systems Distribute Network Functions Across All Connected Devices, Eliminating The Need For A Dedicated Server.
- Each Device Functions Both As A Client And A Server, Enabling Resource Sharing And Collaboration Among Peers.
- Common Examples Of Peer-To-Peer NOS Include Windows Peer-To-Peer Networking And Apple Bonjour.
Network Operating Systems’ Advantages
Centralized Management:
- NOS Provides A Centralized Platform For Managing And Administering Network Resources, Simplifying Tasks Such As User Authentication, Access Control, And Resource Allocation.
- Centralized Management Enhances Efficiency, Reduces Administrative Overhead, And Ensures Consistency Across The Network.
Enhanced Cooperation
- By Facilitating Resource Sharing And Communication Among Connected Devices, NOS Fosters Collaboration And Teamwork Within Organizations.
- Users Can Easily Share Files, Access Shared Printers, And Collaborate On Projects, Regardless Of Their Physical Location.
Enhanced Security:
- NOS Implements Robust Security Mechanisms, Such As User Authentication, Access Control, Encryption, And Intrusion Detection, To Safeguard Network Resources Against Unauthorized Access And Cyber Threats.
- Centralized Security Management Enables Administrators To Enforce Security Policies And Monitor Network Activity Effectively.
Flexibility And Scalability:
- Network Operating Systems Are Designed To Accommodate The Growth And Expansion Of Network Infrastructures.
- They Offer Scalability And Flexibility, Allowing Organizations To Add New Devices, Users, And Resources To The Network Seamlessly.
Uses Of Network Operating Systems In Real World Applications
Enterprise Networks:
- In Large-Scale Enterprise Environments, Network Operating Systems Are Deployed To Manage Complex Networks Comprising Multiple Servers, Workstations, And Devices.
- They Facilitate Resource Sharing, User Authentication, And Centralized Management, Supporting Diverse Business Operations And Workflows.
Education Institutions:
- Educational Institutions Leverage Network Operating Systems To Support Collaborative Learning Environments And Administrative Functions.
- NOS Enables Students And Faculty To Access Shared Resources, Collaborate On Projects, And Communicate Effectively Within The Academic Community.
Small Business Networks:
- Small Businesses Deploy Network Operating Systems To Establish Cost-Effective And Efficient Network Infrastructures.
- NOS Enables Resource Sharing, Centralized Management, And Secure Communication, Empowering Small Businesses To Enhance Productivity And Streamline Operations.
Home Networks:
- Even In Home Environments, Network Operating Systems Play A Role In Enabling Connectivity And Resource Sharing Among Household Devices.
- Home Users Utilize NOS To Share Files, Printers, And Internet Access Among Family Members And Devices, Creating A Connected Ecosystem Within The Home.
Conclusion
Modern Computer Networks Are Supported By Their Network Operating System, Which Makes It Easier To Administer, Share, And Communicate Across A Variety Of Situations. With Its Wide Range Of Features, Advantages, And Useful Applications, Network Outage Services (NOS) Significantly Contributes To Increased Efficiency, Productivity, And Collaboration Across A Number Of Domains, Including Home And Business Networks. Network Operating Systems Will Play A Crucial Role In Facilitating Seamless Connectivity And Helping Businesses And Individuals To Prosper In The Digital Age As Long As Technology Continues To Advance.

